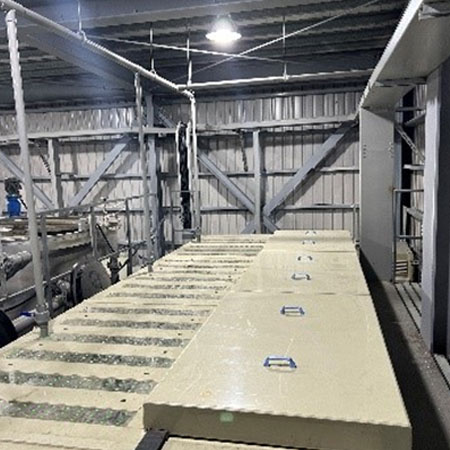
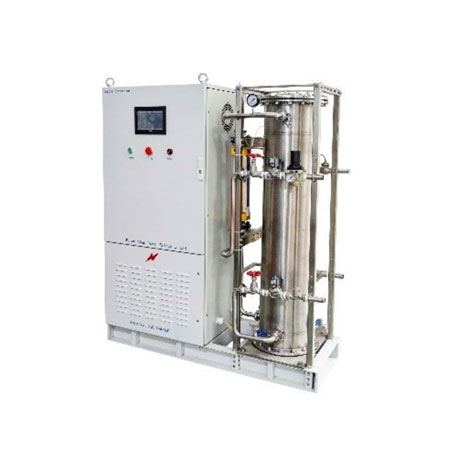
Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Equipment
Equipment Principle
Advanced oxidation technology (AOP) generates strong oxidizing radicals (OH·) under the conditions of light, electricity, catalysts, etc., gradually decomposing macromolecular organic matter into small molecules, effectively reducing wastewater COD. It has a fast reaction rate and is widely used. Advanced oxidation technologies mainly include Fenton oxidation, ozone oxidation, electrochemistry, photocatalysis, etc. Electrocatalytic oxidation uses catalytically active electrode materials to perform electrolysis reactions. The anode can directly oxidize organic matter, and at the same time, it can also generate strong oxidants such as OH·, which can be released into water for indirect oxidation. The selection of electrocatalytic anode materials is crucial. Compared with noble metal electrodes such as Pt, titanium-based metal oxide electrodes are lower in cost and have good catalytic performance and stable reaction efficiency.
Advanced oxidation technology, also known as deep oxidation technology, is based on the use of electricity, light irradiation, catalysts, and sometimes combined with oxidants to produce highly active free radicals (HO•) in the reaction. Through the interaction between free radicals and organic compounds—via adduction, substitution, electron transfer, bond breaking, etc.—the macromolecules in the water and refractory organic matter can be oxidized and degraded into low-toxic or non-toxic small molecular substances, or even directly degraded into CO2 and H2O. Chemical oxidation technology is often used as a pretreatment for biological treatment. Generally, under the action of a catalyst, chemical oxidants are used to treat organic wastewater to improve its biodegradability, and the organic matter in the wastewater is directly oxidized and degraded to stabilize it.
Features
1. It can treat polluted water that is difficult to decompose chemically and biologically.
2. The oxidation rate of organic matter is quite fast, and the required residence time is short, about 1 to 2 hours is enough, while general biological treatment takes about 24 to 48 hours. Due to the short reaction time, the relative reaction tank volume does not need to be too large, thus saving space.
3. The operation is flexible, and the operating conditions can be changed according to the quality of the incoming water to increase the treatment capacity. However, biological treatment is difficult to operate flexibly.
4. Within the design allowable range, the treatment system can handle higher pollution values by simply increasing the dosage.
5. It has strong oxidizing power and can handle a variety of toxic substances, improving the treatment efficiency of COD, ammonia nitrogen, and nitrate nitrogen, and enhancing biodegradability.
Application scope
The food industry, dyeing and finishing industry, domestic sewage, chemical manufacturing, metal processing, metal surface treatment, electroplating industry, and other wastewater treatment. It is suitable for other difficult-to-treat high-concentration wastewater, marine oil field wastewater, printing and dyeing wastewater, high-concentration leachate, and wastewater rich in ammonia nitrogen, containing cyanide and other organic matter with high concentration, complex components, many refractory substances, and high color. It can effectively form hydroxyl radicals with extremely strong oxidizing ability, which can decompose persistent organic pollutants into non-toxic biochemically degradable substances, or completely mineralize them into substances such as carbon dioxide or carbonates.
Performance cases

Diverse specifications and customization
The products can provide planning services and professional technology to solve customer problems according to the different needs of customers.
 繁體中文
繁體中文 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Русский
Русский Português
Português Italiano
Italiano हिन्दी
हिन्दी Español
Español Nederlandse
Nederlandse العربية
العربية Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia বাঙ্গালী
বাঙ্গালী Türk
Türk

